Description
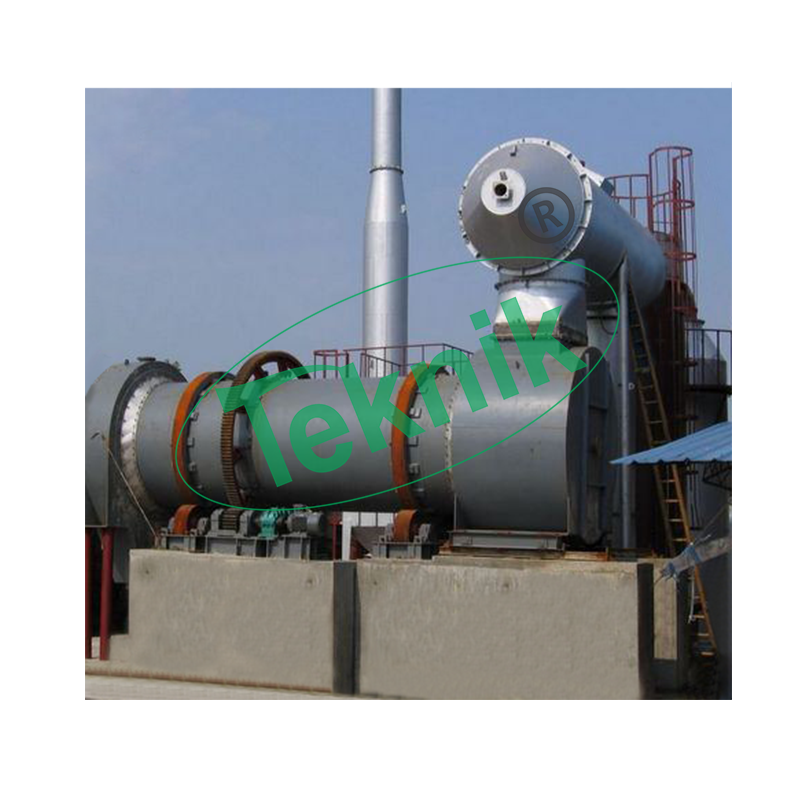
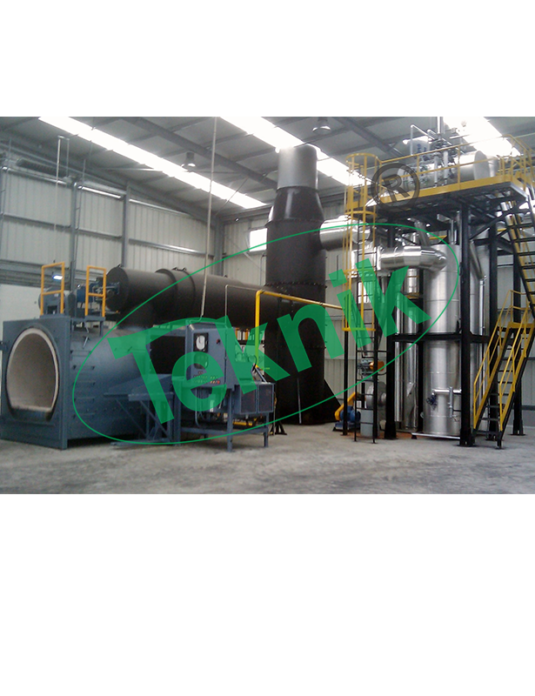
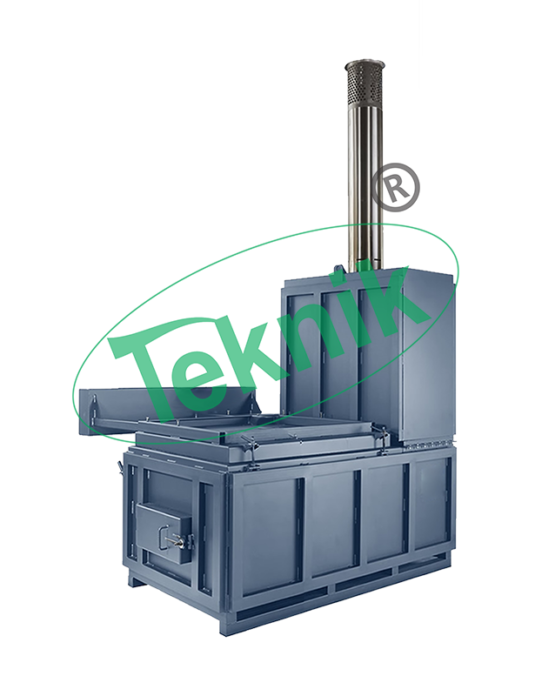
Rotary Kiln is a pyro-processing device used to raise materials to a high temperature (calcinations) in a continuous process. The kiln is a cylindrical vessel, inclined slightly to the horizontal, which is rotated slowly about its axis. Some of the most common kiln applications in use:
- Mineral Roasting
- Proppant Sintering
- Gypsum and Bauxite Calcining
- Waste Incineration
- Desorption of Soil Contaminants
- Upgrading of Phosphate Ores
- Waste Lime Recovery
- Catalyst Activation
- Activated Carbon Production & Re-Activation
- Plastics Processing
- Ceramics Processing
Rotary kilns have become the backbone of many new industrial processes that make the world a more efficient and sustainable place. As new applications for rotary kilns continue to be developed, much experimental work is being done, prompting many questions and the need for further research and development. A rotary kiln is comprised of a rotating cylinder (called the drum), sized specifically to meet the temperature and retention time requirements of the material to be processed. The kiln is set at a slight angle, in order to allow gravity to assist in moving material through the rotating cylinder. Rotary kilns can be either of the direct-fired type, or the indirect-fired type (sometimes referred to as a calciner). In a direct-fired kiln, a process gas is fed through the drum, processing the material via direct contact. In an indirectfired kiln, material is processed in an inert environment, and is heated through contact with the shell of the kiln, which is heated from the outside to maintain an inert environment.
** Note:-The content of the product and specification are subject to change without prior notice for continuous improvement.